
The Cambridge in Colour site has calculations and demonstrations of diffraction spreading at different f-numbers. But if the aperture is small enough, then diffraction can spread the image onto neighboring pixels and constitute the limit on the resolution of the image.
DIFFRACTION LIMITED TELESCOPE FREE
If the image is in focus and free of visible affects of lens aberrations, then it may be that it will fit on one pixel. At left is an attempt to show the effect of diffraction on such imaging in cases where the diffraction is the phenomenon that limits the resolution. While perfect imaging of the source would be smaller perfect circles of light, this shows the smearing of the light by diffraction into the bullseye patterns.įor modern digital photography where the images are projected onto a CCD, the information is collected on pixels of the digital detector. Your eye sees the characteristic bullseye distribution of light as illustrated below. This shows the intensity curves for the radial distribution of the diffracted light for different separations. A team of scientists has developed a way of overcoming the diffraction limit of telescopes, which has the potential to significantly improve the angular. Presuming that diffraction is the determining factor, then the generally accepted criterion for the minimum resolvable detail is the Rayleigh criterion. If you are imaging two points of light, then the smallest separation at which you could discern that there are two could reasonably be used as the limit of resolution of the imaging process. But if the aperture is made too small, the effects of the diffraction will be large enough to begin to reduce that sharpness, and you have reached the point of diffraction-limited imaging. As a matter of general practice in photographic optics, the use of a smaller aperture (larger f-number) will give greater depth of field and a generally sharper image. Its diffraction-limited images are a hundred times sharper than from wide-field ground-based telescopes and extend over much if not all the field, 40 arcmin diameter at 500 nm wavelength, for example. One nds a combined interference and diffraction pattern on the screen. A monochromatic light of wavelength 450 nm is incident on the double-slit. If an image is made through a small aperture, there is a point at which the resolution of the image is limited by the aperture diffraction. A 20 m space telescope is described with an unvignetted 1 field of viewa hundred times larger in area than fields of existing space telescopes. Two slits of width 2m 2 m, each in an opaque material, are separated by a center-to-center distance of 6m 6 m. It does not store any personal data.Diffraction-Limited Imaging Diffraction-Limited Imaging The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. telescope is diffraction limited if it meets the Rayleigh limit - which specifies the separation in arc seconds of two equally-bright binary stars which appear to be just touching as being equal to 140 divided by the aperture in mm.

On the other hand, at three times lower magnification (P3), the 3-minute coma blur field radius also triples, to 1.8mm, with the coma this far off now somewhat worse than diffraction limited. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". At the very edge, coma is only about 1/3 larger than diffraction limited, or about 0.55 wave P-V, with the angular size of about 10 arc minutes. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. Invest in Diffraction Limited controls to help protect your valuable equipment from inclement weather and unreliable control systems. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". Your telescope likely has diffraction-limited optics and a high-value imaging camera or spectrograph.
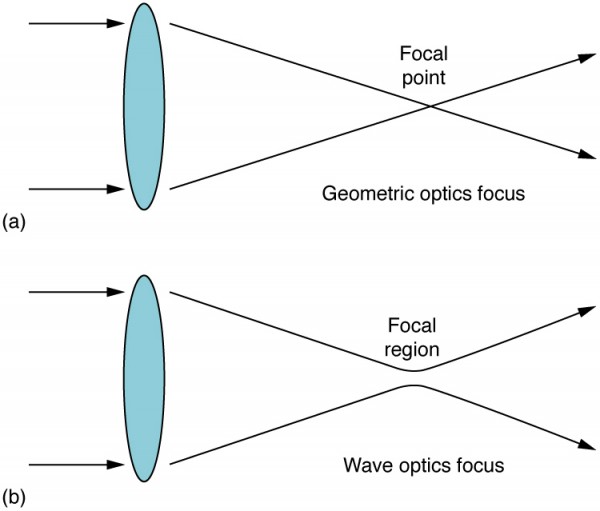

Diffraction by a circular aperture causes a point source of light to be surronded. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The limit to the angular resolution of a telescope is set by diffraction. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Assuming light of 500 nm wavelength and neglecting air turbulence, determine the size of details can be resolved by the telescope. A diffraction-limited telescope with a 7.6-cm aperture is aimed at target 12.5 km away. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Use 550 nm for the wavelength of the light from the stars.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
